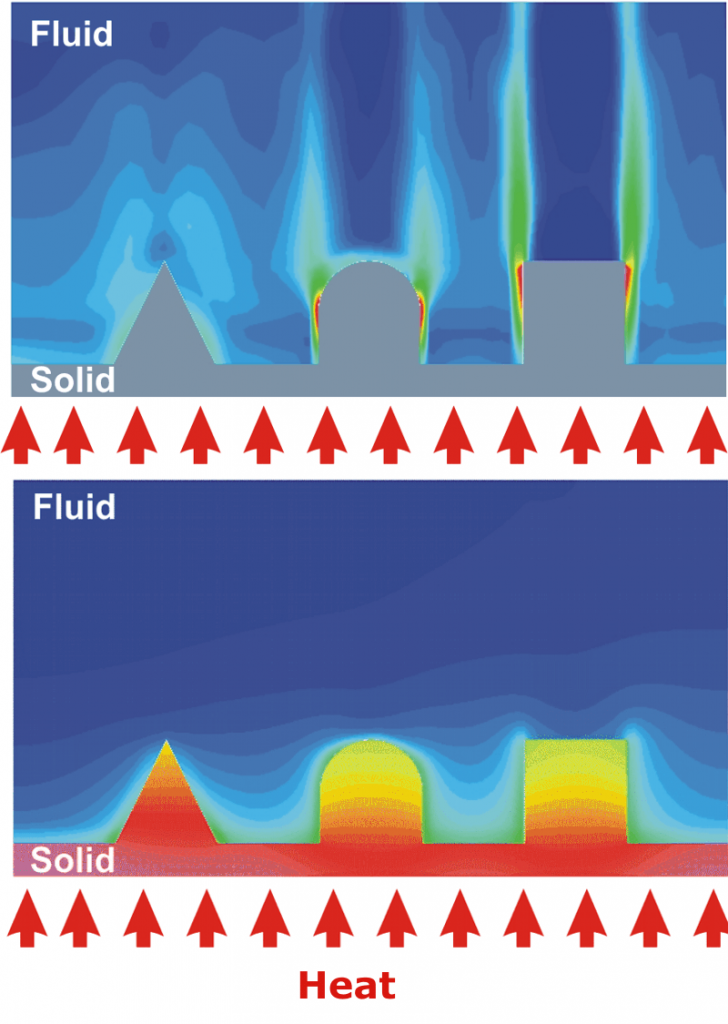
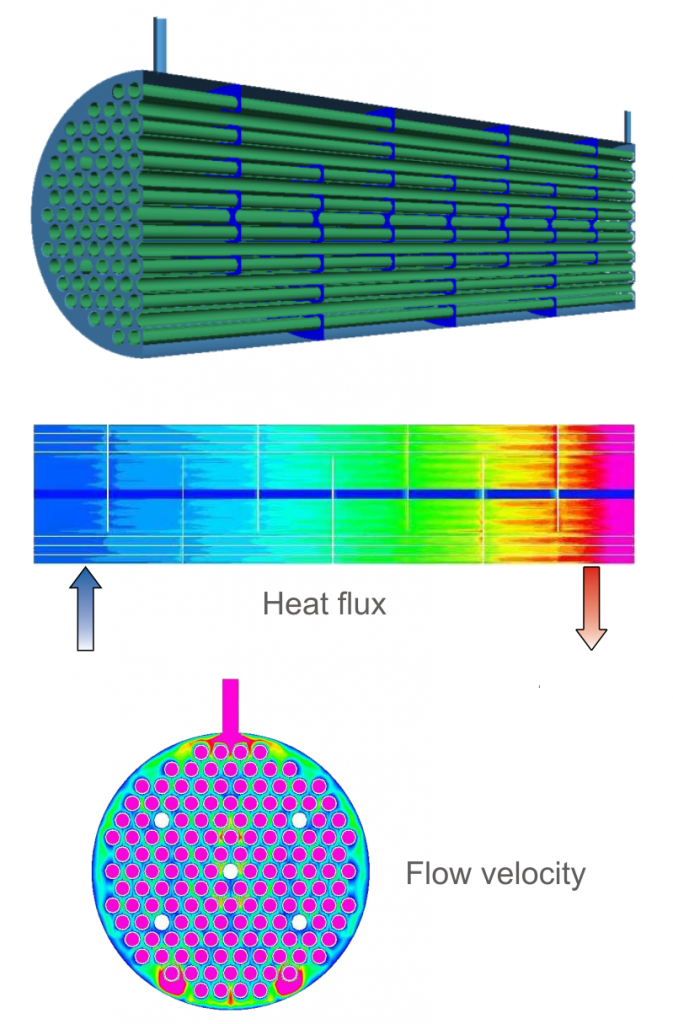
In order to optimize the efficiency of a heat exchanger, i.e. to heat up the material flow to be heated as much as possible and to cool down the other material flow as much as possible, the analysis of the thermal processes in the heat exchangers with special consideration of a uniform inflow, an effective heat transfer and the reduction of the thermal component stress can provide important insights.
By means of simulation of global and local flow conditions and temperature distributions, taking into account free convection or mixed convection, temperature-dependent material values and non-Newtonian rheological behaviour, even the most complicated physical conditions can be analysed. This concerns, for example, evaporation processes at the heat-transferring wall as well as the combination of a laminar and a turbulent flowing medium. Structural mechanical analyses allow the strength properties of the walls and internal structures to be determined. Detailed three-dimensional and time-dependent data on velocity and temperature distributions as well as on heat flow density are available as a result for the entire heat exchanger.